Recommended Products
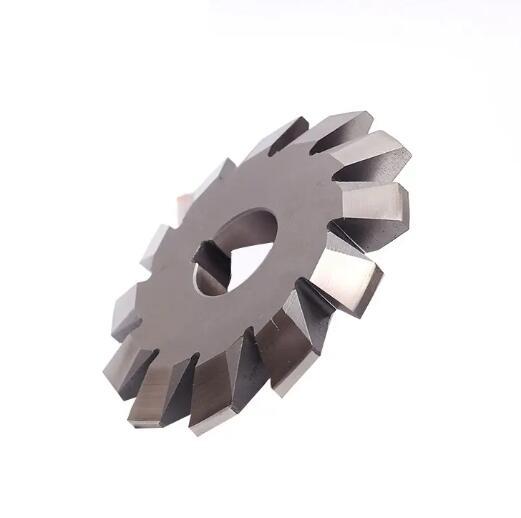
Gear cutters are precision tools used in the manufacture of gears. Their primary purpose is to create the desired gear teeth on gear blanks through cutting processes. Gear cutters are widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, mechanical engineering, and industrial equipment manufacturing. They enable precise control over gear tooth shape, module, and pitch, ensuring the efficiency and stability of gear transmissions.
Usage Methods
1. Preparation:
Select the appropriate type of gear cutter (e.g., hobbing cutter, milling cutter, shaper cutter) based on the type and size of the gear to be machined.
Mount the gear cutter on the corresponding machine, such as a hobbing machine, milling machine, or gear shaping machine. Ensure the cutter is securely installed to avoid vibration or displacement during machining.
2. Workpiece Preparation:
Fix the gear blank on the machine's worktable, ensuring its position and angle are correct.
Align the workpiece and cutter accurately to ensure machining precision. Pre-treat the workpiece, such as cleaning and deburring, to achieve better machining results.
3. Setting Parameters:
Set the machine's cutting parameters, such as speed, feed rate, and cutting depth, according to the gear design drawing. Different materials and tooth shapes require different cutting parameters.
Ensure the lubrication system is functioning properly to reduce cutting heat and tool wear. Choose the appropriate lubricant to ensure smooth cutting.
4. Cutting Process:
Start the machine and proceed with the gear cutting process. Multiple cuts may be necessary to achieve the final tooth shape and dimensions.
Monitor the machining process to ensure the gear cutter and workpiece are operating normally. Adjust parameters as needed to achieve the best machining results. Pay attention to chip formation and machining sounds to assess the machining condition.
5. Inspection and Post-Processing:
After machining, remove the workpiece and perform a quality inspection to ensure the tooth shape accuracy and surface finish meet the requirements. Use measuring tools such as gear gauges and micrometers for precise measurement.
If necessary, perform heat treatment or surface treatment on the gear to enhance its mechanical properties. Choose appropriate surface treatment methods, such as carburizing, nitriding, or coating, based on the gear's application environment.
Usage Precautions
1. Cutter Selection:
Choose the appropriate gear cutter material and type based on machining requirements, ensuring it is suitable for the machining environment and workpiece material. Common materials include high-speed steel and carbide.
2. Proper Installation:
Ensure the gear cutter and workpiece are securely and accurately installed to avoid misalignment or vibration during machining. Use specialized fixtures and tools for installation to ensure stability.
3. Lubrication and Cooling:
Use appropriate lubricants and coolants during the machining process to reduce tool wear and workpiece deformation, extending tool life. Regularly check the cooling system to prevent overheating.
4. Regular Maintenance:
Regularly inspect and maintain gear cutters, replacing worn or damaged tools promptly to ensure machining quality. Clean and maintain the tools to prevent rust and damage.
5. Safety Operation:
Follow safety operating procedures strictly during machining, wearing protective gear to prevent injury from flying chips or machine malfunctions. Regularly train operators to enhance safety awareness.
By correctly using and maintaining gear cutters, machining efficiency and quality can be significantly improved, meeting the demand for high-precision gears in various industrial fields. These measures not only extend the tool's service life but also ensure a safe and stable production process.
Contact: jason@wayleading.com
Whatsapp: +8613666269798
Recommended Products
Post time: Jun-01-2024